FUNCTION OF ORGANELLES AND NON-ORGANELLES
NON-ORGANELLES
1. Plasma Membrane
- Controls the movement of substances in and out of the cell.
 |
| Plant Cell |
 |
| Animal Cell |
2. Cell Wall (only in plants)
- Maintains the shape of a cell.
- Provides support to the plant.
3. Cytoplasm
- A medium that helps in transporting supplies that are required like oxygen, carbon dioxide to the organelles.
 |
| Fluid in the cell is cytoplasm |
ORGANELLES
1. Nucleus
- Controls and regulates all the activities in the cell.
- Contains nucleolus that has chromatin. Chromatin carries genetic information.
 |
| The hair-like structure is chromatin |
 |
| Nucleus |
2. Ribosomes
- Synthesis protein,
- It can be found on the rough endoplasmic reticulum (RER) or small particles move freely around the cell.
3. Endoplasmic Reticulum
a) Smooth endoplasmic reticulum (SER)
- More tubular than RER. Involved in the synthesis and transport lipids.
b) Rough endoplasmic reticulum (RER)
- Studded with numerous numbers of ribosomes. Involved in protein synthesis.
 |
| RER in drawing structure |
 |
| Diagram of RER with attached ribosomes |
4. Mitochondria
- Site of aerobic respiration to produce energy (ATP)
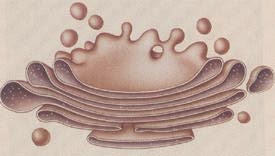
5. Golgi Apparatus
- Responsible for collecting, sorting, processing and packaging mainly carbohydrates, proteins and glycoproteins.
- Abundant in goblet cells which secretes mucus.
 |
 |
| Diagram |
6. Lysozomes
- Contains digestive enzymes to break down complex organic molecules like glucose.
7. Chloroplasts
- For carrying out photosynthesis. Situated at palisade mesophyll cells.
8. Vacuole
- Contains water or dilute solutions of salts and other solutes.
- Maintains turgidity in plants. (permanent vacuole)
9. Centrioles (only animal cell)
- A pair of short microtubules that form spindle fibres during cell division in animal cells.








No comments:
Post a Comment