Hi, everybody! Thank you for visiting our biology blog. :) We, Anis A'lliya (5A) and Siti Mazarina (5B) decided to join the amazing Biology blog. Since this competition is for helping students in schools well, we will try our best to provide as much information about Bio. Also, we will try out best to make things much interesting and simple for you guys to read through. :) Notes and exercises will be provided too! :D See, how cool is it. Last but not least, we'll try our best to use good English language while providing/explaining you guys notes. Structure questions are provided with answers. So, don't you worry on searching it on the net!
THANK YOU!
P/S: We might skip chapters. Sorry! ((Bummer i know))
Saturday, 5 April 2014
Friday, 4 April 2014
Form 4: Chapter 2: Cell Structure and Cell Organisation (part 1)
CELL STRUCTURE AND CELL ORGANISATION
 |
| ANIMAL CELL |
Thursday, 3 April 2014
Form 4: Chapter 2: Cell Structure and Cell Organisation. (part 2)
FUNCTION OF ORGANELLES AND NON-ORGANELLES
NON-ORGANELLES
1. Plasma Membrane
- Controls the movement of substances in and out of the cell.
 |
| Plant Cell |
 |
| Animal Cell |
2. Cell Wall (only in plants)
- Maintains the shape of a cell.
- Provides support to the plant.
3. Cytoplasm
- A medium that helps in transporting supplies that are required like oxygen, carbon dioxide to the organelles.
 |
| Fluid in the cell is cytoplasm |
ORGANELLES
1. Nucleus
- Controls and regulates all the activities in the cell.
- Contains nucleolus that has chromatin. Chromatin carries genetic information.
 |
| The hair-like structure is chromatin |
 |
| Nucleus |
2. Ribosomes
- Synthesis protein,
- It can be found on the rough endoplasmic reticulum (RER) or small particles move freely around the cell.
3. Endoplasmic Reticulum
a) Smooth endoplasmic reticulum (SER)
- More tubular than RER. Involved in the synthesis and transport lipids.
b) Rough endoplasmic reticulum (RER)
- Studded with numerous numbers of ribosomes. Involved in protein synthesis.
 |
| RER in drawing structure |
 |
| Diagram of RER with attached ribosomes |
4. Mitochondria
- Site of aerobic respiration to produce energy (ATP)
5. Golgi Apparatus
- Responsible for collecting, sorting, processing and packaging mainly carbohydrates, proteins and glycoproteins.
- Abundant in goblet cells which secretes mucus.
 |
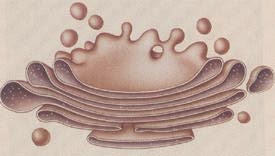 |
| Diagram |
6. Lysozomes
- Contains digestive enzymes to break down complex organic molecules like glucose.
7. Chloroplasts
- For carrying out photosynthesis. Situated at palisade mesophyll cells.
8. Vacuole
- Contains water or dilute solutions of salts and other solutes.
- Maintains turgidity in plants. (permanent vacuole)
9. Centrioles (only animal cell)
- A pair of short microtubules that form spindle fibres during cell division in animal cells.
Wednesday, 2 April 2014
Form 4: Chapter 2: Cell Structure and Cell Organisation. (part 3)
Is everything working well? We hope that you understand better by seeing those diagrams/ pictures we provide you and explaination. But, if you still cant understand by reading and seeing diagrams... Well... We have VIDEOS for you! :) It makes learning much more fun and simpler. We'll be giving you links to those videos, and i really hope it will help you guys understand wayyyyyy better. Choose your subtopics and here are the links:
(Just click on the links and will it will bring you to another tab)
Cell Structure and Function
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=rdtpbZYS_6A&noredirect=1 (part 1)
http://www.youtube.com/watch?feature=player_embedded&v=PVaWnQKa4rA (part 2)
Differences between Animal cell and Plant cells/ Density of Organelles
http://www.youtube.com/watch?feature=player_embedded&v=H9qYhGqYhvs
Cell Organisation in Humans and Animals
http://www.youtube.com/watch?feature=player_embedded&v=KknTjOD6eyM
Cell Organisation in Plants
http://www.youtube.com/watch?feature=player_embedded&v=R7WV44wrXZs
(Just click on the links and will it will bring you to another tab)
Cell Structure and Function
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=rdtpbZYS_6A&noredirect=1 (part 1)
http://www.youtube.com/watch?feature=player_embedded&v=PVaWnQKa4rA (part 2)
Differences between Animal cell and Plant cells/ Density of Organelles
http://www.youtube.com/watch?feature=player_embedded&v=H9qYhGqYhvs
Cell Organisation in Humans and Animals
http://www.youtube.com/watch?feature=player_embedded&v=KknTjOD6eyM
Cell Organisation in Plants
http://www.youtube.com/watch?feature=player_embedded&v=R7WV44wrXZs
Tuesday, 1 April 2014
Exercises for Chapter 2 Form 4! :D
The structure of and animal cell

Diagram 1
1. Name the structures A to D
A:_______________________
B:_______________________
C:_______________________
D:_______________________
2. This animal cell has the role of secreting enzymes. Describe th functional relationship between structures A, D and E in the secretion of enzymes.
___________________________________________________________________________
(HOTS)
3. Distinguish between 'tissue' and 'organ'. giving an example of each in an animal cell.
___________________________________________________________________________
Answers:
1. A: RER
B: nuclear membrane
C: mitochondria/mitochondrion
D: Golgi apparatus
2. The RER, A manufactures and transports proteins which are bound into vesicles and transported to D, the Golgi apparatus. The Golgi apparatus packages, modifies and processes the proteins which are enzymes and send them in secretory vesicle E where it moves towards the plasma membrane and fuses with plasma membrane then releases its contents outside the cell.
3. - A tissue is a collection of similar cells which performs a similar function. Example: Epithelial tissue.
- An organ consists of two or more different tissues types working together as a unit, to perform a particular function. Example: Heart.
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)









